What is blockchain translation and localization?
Blockchain translation and localization refers to adapting blockchain technology and applications to different languages and cultures. This includes translating the user interface, documentation, and other content into multiple languages and ensuring that the technology complies with local laws and regulations.
Given the recent “cryptopocalypse,” blockchain translation has become more relevant than ever.
But before we delve into the many benefits of localization, let’s briefly discuss blockchain technology.
- What is blockchain?
- Why has it become so popular?
- What are the key challenges facing the blockchain industry?
Blockchain technology has been touted as one of the most revolutionary pieces of tech to have been invented; however, despite its hype, it largely remains an underused technology. Contrary to popular belief, blockchain has been around since the late 60s, and its adoption rate has been slowly creeping up, year after year. Many hope to see it become part of our mainstream financial systems this decade.
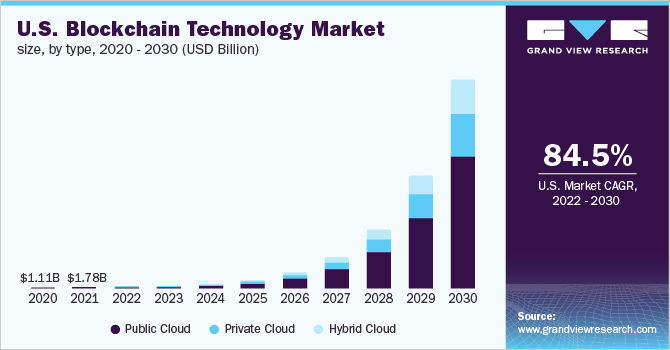
In fact, according to Grandview Research, the global blockchain market is expected to grow by a whopping 85.9% between 2022 and 2030. Furthermore, the recent legalization of cryptocurrencies in several countries coupled with its adoption in large companies like Paypal is likely to drive this momentum forward.
Blockchain – A global phenomenon
It almost goes without saying, but blockchain isn’t a regional technology, limited to rich tech-friendly countries, far from it. It is intended to disrupt worldwide networks and create a decentralized world.
For instance, just in the past five years, over 23 different governments started blockchain pilot programs. Another 12 are developing their own programs as well, including the massive Chinese government. As you can imagine, these countries are from every single continent in the world.
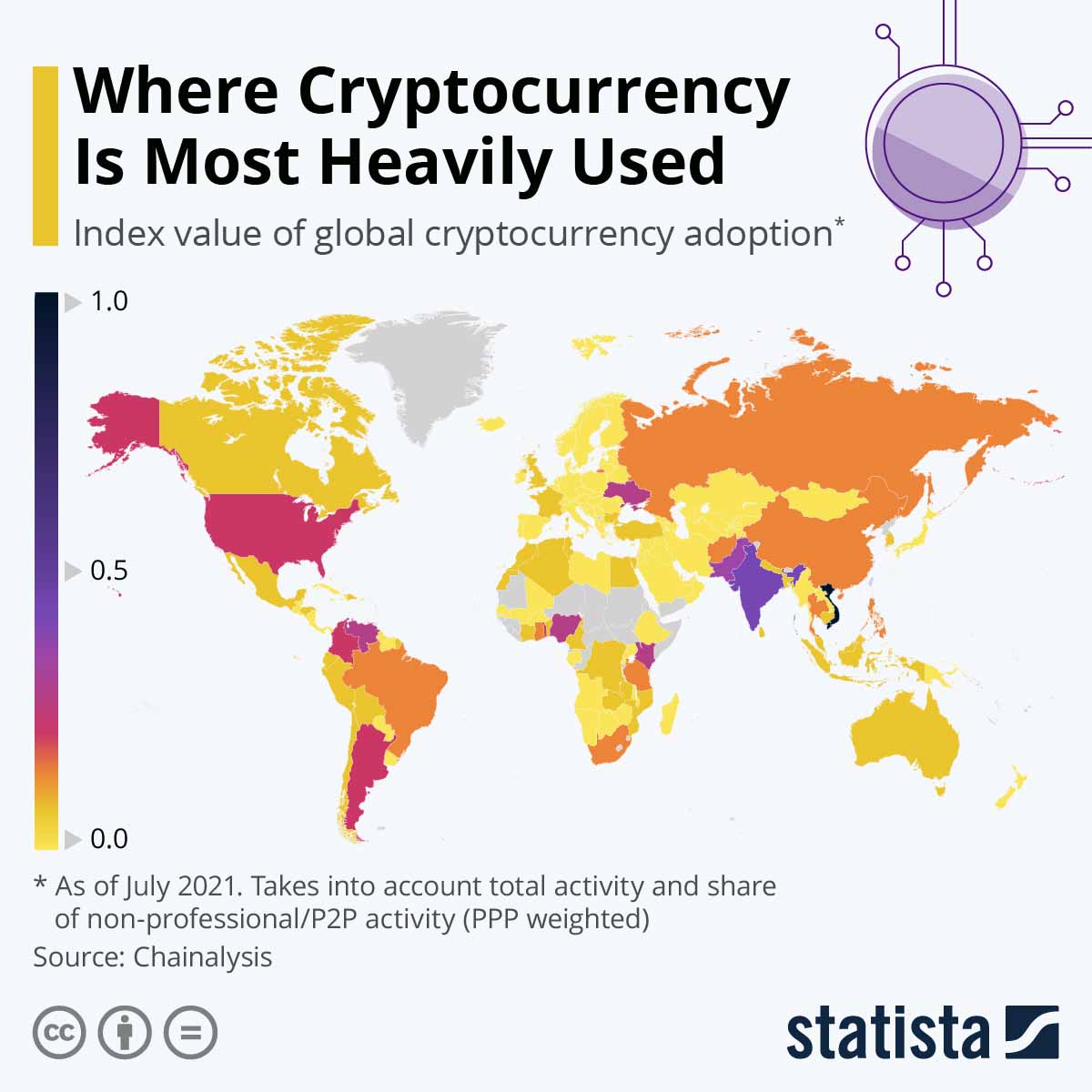
That being said, not all blockchain applications are moving at the same pace. For instance, as you can see in the map below, cryptocurrencies are lagging a bit behind. However, even with their slower adoption rate, you can clearly see that crypto usage is global.
Although it is global in its reach, the barriers to its adoption are local in their nature. Blockchain is a foundational technology, and to become a disruptive one it needs to get localized.
But before we delve into the many hurdles it needs to overcome, let’s first agree on some blockchain fundamentals.
What is blockchain?
Blockchain is distributed database that is shared across a network of computers. And in simpler terms, a decentralized immutable digital ledger. It is a sophisticated ledger, but a ledger nonetheless.
Although blockchain and cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, have become synonymous in the zeitgeist, they are not the same thing. In fact, cryptocurrencies are just an application of blockchain technologies.
If it’s just a ledger, what makes blockchain valuable?
Because it is a decentralized immutable record of all the transactions that occur within it.
For instance, when you buy something today, the information about that transaction is largely recorded by a single institution (a bank), making you beholden to said institution and its failings. If they make a mistake in your records, you don’t have a reliable way of verifying that record aside from trusting the bank and its internal auditing processes.
However, with blockchain that same transaction is recorded and overseen by all parties in that network, making it unalterable. If one party tries to change the record, all parties can see it and they can keep a record of the change. By being dispersed, the information (transaction) on that network can’t be tampered with. The sheer transparency of blockchain protects you from mistakes or fraudulent activity.
Each member of the chain strengthens the verification process of the entire blockchain. The more users it has, the more tamper-proof it becomes. This distributed network creates more transparency and protects you against fraudulent activity or simple record-keeping mistakes.
Financial institutions
Although this particular group has become more accepting of blockchain technology, they are much more resistant to cryptocurrencies. After all, considering the lack of transaction fees with crypto, widespread adoption of these technologies could reduce their profits and will require them to change their business model.
Governments have also been historical antagonists in the blockchain and cryptocurrency story. Despite their recent pilot programs, many governments are still dragging their feet and remain unconvinced of the usefulness of the technologies.
Consumer-facing businesses
The average business still doesn’t accept cryptocurrencies as payment. Granted, we are likely to see some positive changes in the upcoming few years, but this group’s adoption of crypto will depend on what financial institutions and governments decide to do.
Consumers
This group is where proper localization can help you the most. They are typically much more inclined to adopt blockchain. That being said, for widespread adoption, the two previous groups must be convinced. After all, it doesn’t matter how many consumers decide to use the technology if consumers cannot use it in their transactions, they will have to rely on traditional financing systems.
Now that you understand the sources of pushback a bit more, let’s discuss the blockchain challenges.
Challenges to blockchain adoption
1. Lack of trust
As I’ve mentioned previously, despite the global nature of blockchain, it is far from being a mainstream technology. There are many different reasons for that, but the truth about crypto is that it’s an issue of trust.
Individual users are worried about the security risks that come with a blockchain network—and for good reason. After all, even someone as clever as Steve Wozniak got scammed out of $70,000 in bitcoin. If someone as technologically savvy as the co-founder of Apple has a hard time with blockchain, then what chance do the rest of us have?
The technology is new and complex enough that users are too afraid to use it. The fear of losing their life’s savings in a few clicks is understandable. It behooves you to improve communication with your target consumers and create compelling content that can truly explain how to operate the technology safely.
2. Legal challenges
Despite recent developments, one of the key blockchain issues is of a legal and regulatory nature. Like all new technologies, there is no regulatory framework in place to handle blockchain.
To make matters worse, as I’m sure you know, governments and their legislative branches are not known for their speed and adaptability. Bureaucracy being what it is, it often takes years for a governmental agency to catch up, and in the meantime, blockchain applications find themselves curtailed or outright banned.
Liability
As we discussed, the decentralized nature of blockchain is a key selling point of the technology; however, it also creates a clear downside—assigning liabilities.
Due to its chainlike structure, blockchain is almost failure-proof. But, life being life, as failure-proof as it may be, there will come a day when a failure does occur. At that point, who is liable for such a failure?
With the current financial system, the liable parties are clear. But in a distributed network with so many different members, who is liable? It’s hard to tell.
3. Data security
Tied to the previous point, in a decentralized system it’s quite hard to determine who owns the data in the network and which laws apply to it. For instance, if 10% of the members are from India, while another 10% are in the United States, which laws apply? The American or Indian ones?
Furthermore, there is no clear path forward with privacy. The data in a public blockchain is accessible to every member of the chain. Even if a country were to require that said data should be removed, it can’t be done without altering the chain itself.
4. Technical knowledge
Due to its high-tech nature, blockchain remains difficult to understand for a large chunk of potential consumers. The average individual isn’t equipped with the know-how to grasp what P2P means, or the subtle differences that blockchain brings to the table.
To make matters worse, most blockchain applications are not in the native languages of the target users, further exacerbating this “knowledge” gap.
5. Cultural differences
Although societies across the world are becoming more tech-friendly, there is still a substantial number of individuals that prefer human solutions.
The notion of a cashless society is not appealing to this subgroup and it will likely require substantial marketing efforts to convince them to join a blockchain application. These are individuals that still prefer going to a bank physically rather than relying on any online means.
Blockchain translation to the rescue
Although there are many different advantages to localizing your blockchain application, there are some industry-specific benefits you stand to gain.
Building trust
As we have discussed, trust is where blockchain is lacking the most and we believe that it’s in this very aspect that localization can help the most.
Survey after survey, consumers are clearly telling us that they do not trust a website that is not in their native language. That is especially true for transactional sites such as crypto companies.
If you want end-users to start trusting your services, you have to localize them—it is not optional.
Reduce friction
Tied to the previous point, blockchain suffers from a high knowledge entry point so why exacerbate it by providing your product in a language that your target consumer is not comfortable with.
Human beings are convenience-driven; we often select what’s available not what’s best. If you want to make your product more competitive, you have to reduce friction until picking it becomes effortless.
It’s not just about the language, you have to design the user interface with your target’s preferences in mind. For instance:
- Do they scroll through your app or do they prefer links?
- Do they read from left to right or right to left?
- What about the size of the script?
- Which tone do they prefer?
These are just some of the many questions you should ask yourself to figure out the best path ahead.
Bridge the cultural gap
Aside from their browsing habits, you also have to embrace their cultural preferences. For instance, if you wish to target users in Kazakhstan you should probably leverage their preference for micro-payments.
If you put it at the forefront of your marketing campaign, you may craft enough of a convincing case to overcome their distrust of blockchain. After all, low to zero commissions can be a very convincing selling point.
On the other hand, if you are targeting users in the southern states of the United States, you may want to leverage their growing distrust of large financial institutions by advertising the transparency features of blockchain applications.
Blockchain translation is important, but if not done right, it can cause problems. You can try to translate your app by yourself, but it’s hard, even with tools like Google Translate or ChatGPT.
There are tricky technical parts about blockchain that experts understand best. If unsure, you can request a quote and chat with our team before deciding on your translation needs.
Also, if you want to learn more about different translation methods and tools, check out our guide on the top blockchain translation tools.